Brain-Inspired Algorithms and Machine Learning
Overview
Our research theme on brain-inspired algorithms and machine learning focuses on developing computational models and techniques that emulate the cognitive processes of the human brain. By leveraging insights from neuroscience, we aim to create more efficient, adaptive, and intelligent systems capable of solving complex problems across various domains.
Key areas of our research include designing innovative neural network architectures, developing advanced learning algorithms inspired by synaptic plasticity, and creating neuromorphic computing systems that replicate the brain's parallel processing capabilities.
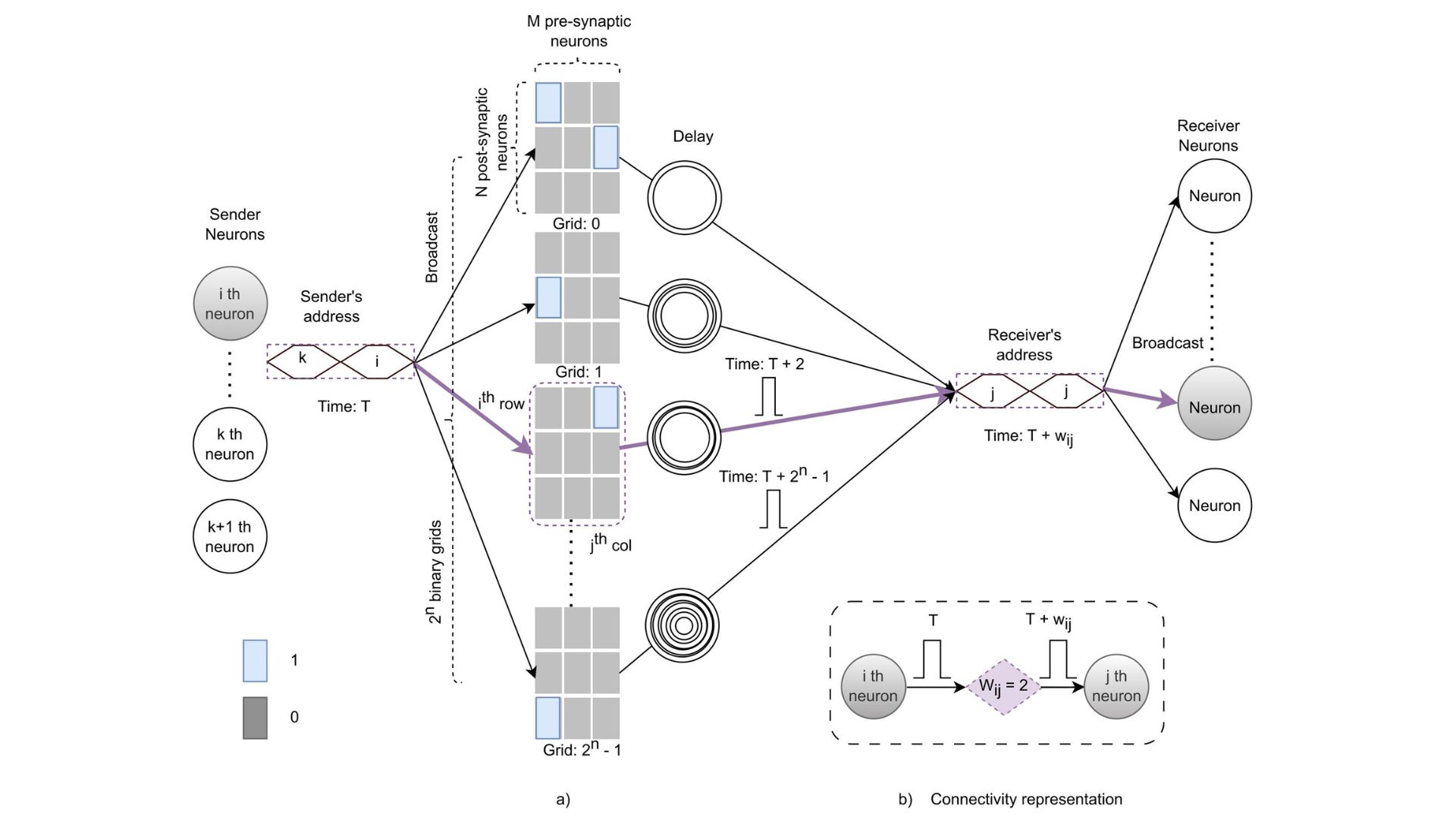
Realisation of Time-to-Event Margin Propagation in Address Event Representation
Selected Publications
- Mangalwedhekar, R., Singh, N., Thakur, C. S., Seelamantula, C. S., Jose, M., & Nair, D. (2023). Achieving nanoscale precision using neuromorphic localization microscopy. Nature Nanotechnology, 18(4), 380-389.
- Srivatsav, R. M., Chakrabartty, S., & Thakur, C. S. (2023). Neuromorphic Computing With Address-Event-Representation Using Time-to-Event Margin Propagation. IEEE Journal on Emerging and Selected Topics in Circuits and Systems, 13(4), 1114–1124.
- Annamalai, L., & Thakur, C. S. (2024). EventF2S: Asynchronous and Sparse Spiking AER Framework using Neuromorphic-Friendly Algorithm. arXiv preprint arXiv:2402.10078.
- Annamalai, L., Ramanathan, V., & Thakur, C. S. (2024). EventMASK: A Frame-Free Rapid Human Instance Segmentation with Event Camera Through Constrained Mask Propagation. IEEE Robotics and Automation Letters.
- Annamalai, L., & Thakur, C. S. (2024). EventASEG: An Event-Based Asynchronous Segmentation of Road With Likelihood Attention. IEEE Robotics and Automation Letters.
- Annamalai, L., Ramanathan, V., & Thakur, C. S. (2022). Event-LSTM: An unsupervised and asynchronous learning-based representation for event-based data. IEEE Robotics and Automation Letters, 7(2), 4678-4685.
- Annamalai, L., Chakraborty, A., & Thakur, C. S. (2021). EvAn: neuromorphic event-based sparse anomaly detection. Frontiers in Neuroscience, 15, 699003.
- Molin, J. L., Thakur, C. S., Niebur, E., & Etienne-Cummings, R. (2021). A neuromorphic proto-object based dynamic visual saliency model with a hybrid FPGA implementation. IEEE transactions on biomedical circuits and systems, 15(3), 580-594.
- Mangalore, A. R., Seelamantula, C. S., & Thakur, C. S. (2020). Neuromorphic fringe projection profilometry. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 27, 1510-1514.
- Xu, Y., Afshar, S., Wang, R., Cohen, G., Singh Thakur, C., Hamilton, T. J., & van Schaik, A. (2021). A biologically inspired sound localisation system using a silicon cochlea pair. Applied Sciences, 11(4), 1519.
- Krishna, A., Mittal, D., Virupaksha, S. G., Nair, A. R., Narayanan, R., & Thakur, C. S. (2021). Biomimetic FPGA-based spatial navigation model with grid cells and place cells. Neural Networks, 139, 45-63.
- Thakur, C. S., Wang, R. M., Afshar, S., Hamilton, T. J., Tapson, J. C., Shamma, S. A., & van Schaik, A. (2015). Sound stream segregation: a neuromorphic approach to solve the “cocktail party problem” in real-time. Frontiers in neuroscience, 9, 309.
- Thakur, C. S., Afshar, S., Wang, R. M., Hamilton, T. J., Tapson, J., & Van Schaik, A. (2016). Bayesian estimation and inference using stochastic electronics. Frontiers in neuroscience, 10, 104.


