FreeRTOS Lab 05
- Demonstrate that the scheduler always selects the highest Ready state task to run
- by using the vTaskPrioritySet() API function to change the priority of two tasks relative to each other.
- Two tasks are created at two different priorities.
- Neither task makes any API function calls that cause it to enter the Blocked state,
- So both are in either Ready or Running state.
- So the task with highest priority will always be the task selected by the scheduler to be in Running state
- Expected Behavior
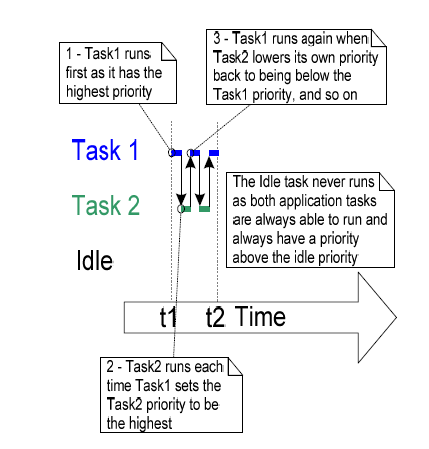
- Task 1 is created with the highest priority to be guaranteed to run first. Task 1 prints out a couple of strings before raising the priority of Task 2 to above its own priority.
- Task2 starts to run as it has the highest relative priority.
- Task 2 prints out a message before setting its own priority back to below that of Task 1.
- Task 1 is once again the highest priority task, so it starts to run and forcing Task 2 back into the Ready state.
- Functions to be Used
- vTaskPrioritySet(xTaskHandle pxTask, unsigned portBASE_TYPE uxNewPriority);
- To be used to change the priority of any task after the scheduler has been started.
- Available if INCLUDE_vTaskPrioritySet is set 1.
- Two parameters
- pxTask: Handle of the task whose priority is being modified. A task can change its own priority by passing NULL in place of a valid task handle.
- uxNewPriority: the priority to be set.
- unsigned portBASE_TYPE uxTaskPriorityGet(xTaskHandle pxTask);
- To be used to query the priority of a task
- Available if INCLUDE_vTaskPriorityGet is set 1
- pxTask: Handle of the task whose priority is being modified. A task can query its own priority by passing NULL in place of a valid task handle.
- Returned value: the priority currently assigned to the task being queried

Recent Comments